Short descriptions of vintage motorcycles – Scott to Zuendapp
Scott

1897, Great Britain. Like many later motorcycle manufacturers, Alfred Scott first became involved with two‑wheelers through bicycles — his first patent in 1897 was for a bicycle rim brake. As early as 1908, Scott motorcycles were equipped with two‑stroke engines. Although famous racers such as Jimmy Simpson and Stanley Woods rode Scott racing models, the marque remained largely unsuccessful in competitive racing.
In 1931 Scott declared bankruptcy. A Scott enthusiast from Liverpool bought the company and continued production under the name “Scott Motor Ltd.” for some years. When the factory closed again in 1945, another enthusiast purchased the remains, renamed the company “Swift” and produced motorcycles under the name “Silk” — until production finally ceased in 1980.
Sunbeam
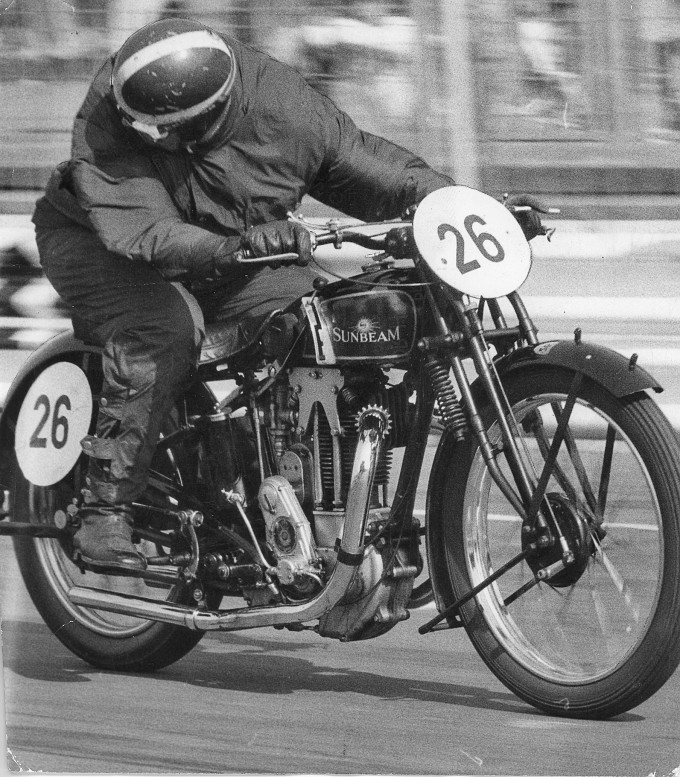

(1790) 1912, Great Britain. The Wolverhampton‑based Sunbeam company proudly mentioned the year 1790 on its catalogues — not for motorcycles, of course, but because the Marston family originally traded in Japanese goods. Bicycles were added to the product range in 1887, cars followed in 1900 using De Dion‑Bouton engines, and finally in 1912 the first Sunbeam motorcycle appeared with a 2¾ hp (349 cc) engine.
Sunbeam motorcycles were regarded as having the finest workmanship and finish of all English singles. The marque won the Senior TT four times — in 1920, 1922, 1927 and 1928. Among the most successful riders were Graham Walker and Charlie Dodson (both English), A. Varzi (Italy), F. Franconi (Switzerland) and Rupert Karner from Austria.
At the end of 1936 Sunbeam was sold to AMC, which already owned the AJS and Matchless marques. After the Second World War attempts were made to revive former glories, but without success. The Sunbeam name disappeared in the early 1960s.
Triumph
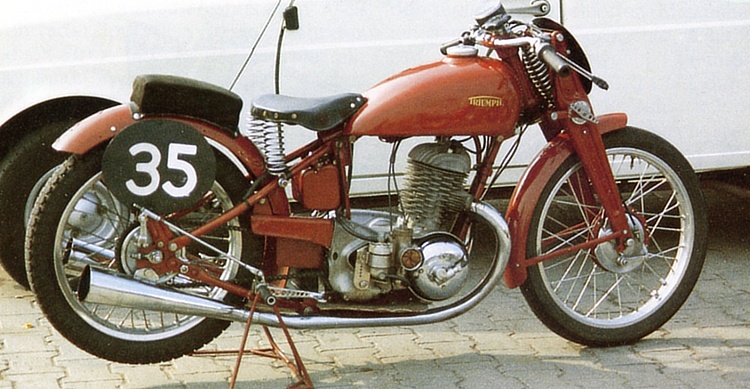
1885, Great Britain. The Triumph marque was founded by German businessman Siegfried Bettmann, who settled in England in 1884. He established his own import–export company, initially working with a Birmingham bicycle manufacturer. Recognising the need for a strong brand name, especially abroad, he chose the name Triumph.
After expanding the business with a German technical expert, they founded the New Triumph Cycle Co. Ltd.. In 1902 the first Triumph motorcycle appeared: a 239 cc machine producing 1¾ hp. Triumph’s early TT successes — for example, five of the first ten finishers in 1908 rode Triumphs — brought financial prosperity.
By 1927 Triumph offered eight motorcycle models, but production was halved the following year in favour of automobile manufacturing. The company’s racing involvement in the 1930s was modest, but after the Second World War Triumph returned with stronger models such as the Grand Prix. Later the company also produced trial engines. In 1951 Triumph was sold to the BSA Group.
Triumph Germany was founded in 1896 in Nuremberg. This partnership lasted until 1929, after which the Nuremberg factory marketed its products abroad under the name TWN.
Velocette

1905, Great Britain. Like Triumph, Velocette has German roots: Johannes Gütgemann, who called himself John Goodman in England, worked for the company “Taylor, Gue & Co.”. In 1905 the firm created a motorcycle named Veloce. Financial difficulties led Goodman to establish his own company with Edward Williams: Veloce Ltd.
From 1929 onwards Veloce produced “Production Racers” for private owners. The KTT Mk I to Mk V models were built between 1929 and 1935. No Mk VI was sold to privateers. In 1938 the Mk VII appeared with a rigid frame, followed in 1939 by the Mk VIII — a true copy of the Junior TT‑winning works machine, fitted with swinging‑arm rear suspension as ridden by Stanley Woods.
Production of the KTT Mk VIII continued from 1947 to 1951, making it one of the most successful 350 cc racing motorcycles. Velocette won the Junior TT in 1947, 1948 and 1949, and the 350 cc World Championship in 1949 and 1950.
In 1971 the company went into voluntary liquidation. English history: www.velocetteowners.com/history/history.html
Victoria
1890, Germany. |
Vincent HRD
1895, Great Britain. |
Wanderer
1886, Germany. |
Zenith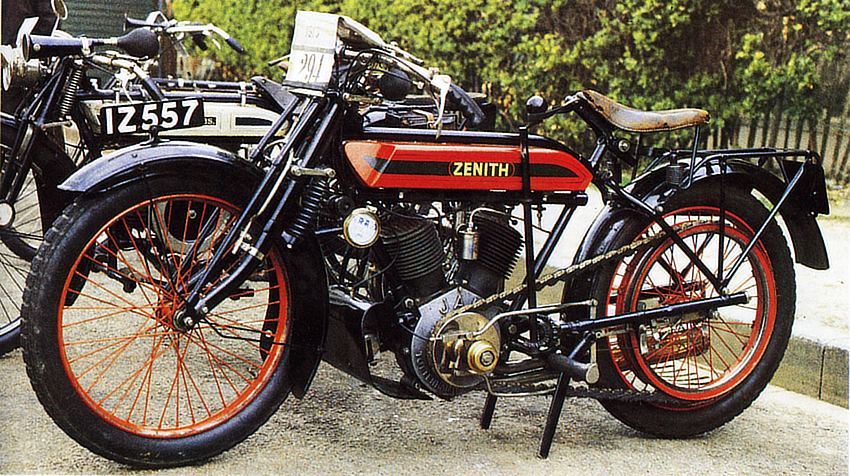
1905, Great Britain. |
Zuendapp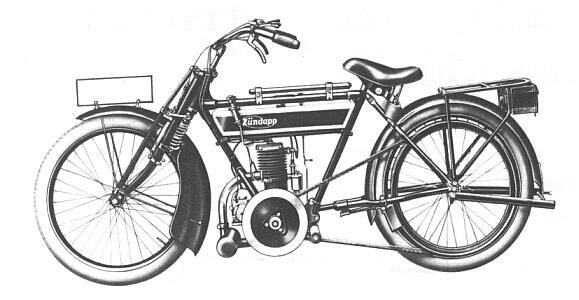
1917, Germany. |